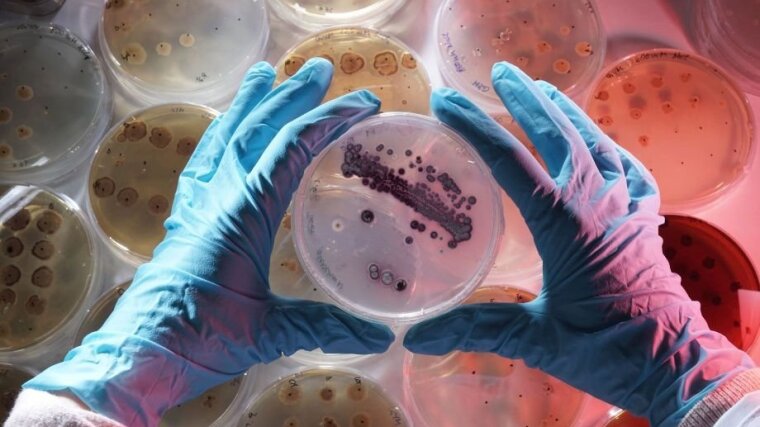
Streptomycetes from a heavy metal containing site in Eastern Thuringia were used to examine the mechanisms of heavy metal resistance with molecular biological methods. Extreme sites with high metal load like the former uranium mining site near Ronneburg showed adaptations of the microorganisms, for example towards 130 mM nickel. In this context, this Streptomyces mirabilis was sequenced with the DMSZ. A transformation system could be established. Resistance genes located on a megaplasmid have been characterized. One of these ones is nreB, which codes for a metal transporter. The heterologous expression of this gene led to improved nickel tolerance – not only in another streptomycete, S. lividans, but also in E. coli. The deletion of the gene resulted in reduced nickel tolerance in the original strain.
Field and pot experiments together with plants and mycorrhizal fungi should allow approaches for the bioremediation of polluted areas. Another focus is the investigation of the bacterial diversity of various habitats, also with regard to the geology of the sites, such as extreme sites with high salt loads or radionuclide-containing waters. Furthermore, the degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by autochthonous microorganisms is being analyzed – also with regard to the use of microorganisms for the gentle remediation of contaminated areas. The formation of biominerals could be characterized with Ni-struvite as well as Cs- and Sr-struvite. This can also play a role during the colonization of extreme habitats as a strategy for reducing local bioavailable salt and heavy metal concentrations.
Colleagues in these projects:
M.Sc. Marlene Höller, M.Sc. Thomas Krauße, M.Sc. Kevin Lenk, M.Sc. Sebastian Pietschmann, M.Sc. Flávio Silva Costa, M.Sc. Marie Harpke.
Alumni: Dr. Andrea Beyer, Dr. Hanka Brangsch, M.Sc. Katja Burow, M.Sc. Benjamin Funai, M.Sc. David Fürst, Dipl.-Biol. Stefanie Gierer, Dr. Götz Haferburg, M.Sc. Michael Klose, Dipl.-Biol. Stefanie Koch, M.Sc. Uwe Lange, Dr. Francesca Langella, Dr. Aileen Meyer, Dr. René Phieler, Dr. Martin Reinicke, Dr. Frank Schindler, Dr. Andre Schmidt, Dr. Astrid Schmidt, Dr. Eileen Schütze, M.Sc. Jennifer Stoiber-Lipp, Dr. Annekatrin Voit, M.Sc. Johanna Ziethe.
Most important publications:
Harpke, M and Kothe, E (2023) Biofilm formation in Gram-positives as an answer to combined salt and metal stress. Journal of Basic Microbiology.
Harpke M, Pietschmann S, Ueberschaar N, Krüger T, Kniemeyer O, Brakhage AA, Nietzsche S, Kothe E (2022) Salt and Metal Tolerance Involves Formation of Guttation Droplets in Species of the Aspergillus versicolor Complex. Genes. 13 (9).
Brangsch H, Höller M, Krauße T, Waqas M, Schroeckh V, Brakhage AA, Bunk B, Sproer C, Overmann J, Kothe E (2022) Extremophile Metal Resistance: Plasmid-Encoded Functions in Streptomyces mirabilis. Applied and Environmental Mirobiology. 88 (11). DOI10.1128/aem.00085-22
Costa FS, Langenhorst F, Kothe E (2022) Biomineralization of Nickel Struvite Linked to Metal Resistance in Streptomyces mirabilis. Molecules. 27 (10). DOI10.3390/molecules27103061
Burow B, Grawunder A, Harpke M, Pietschmann S, Ehrhardt R, Wagner L, Voigt K, Merten D, Büchel G, Kothe E. (2019). Microbiomes in an acidic rock–water cave system. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 366(13), fnz167, https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnz167
Krauße T, Schütze E, Phieler R, Fürst D, Merten D, Büchel G, Kothe E. (2017). Changes in element availability induced by sterilization in heavy metal contaminated substrates: A comprehensive study. J Hazard Mater 370. 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.008.
Meier A, Singh M, Kastner A, Merten D, Büchel G, Kothe E. (2017). Microbial communities in carbonate rocks-from soil via groundwater to rocks. J Basic Microbiol 57, 10.1002/jobm.201600643.
Meier A, Kastner A, Harries D, Wierzbicka-Wieczorek M, Majzlan J, Büchel G, Kothe E. (2017). Calcium carbonates: Induced biomineralization vs. controlled macromorphology? Biogeosciences Discuss 14, 1-21. 10.5194/bg-14-4867-2017.
Schütze E, Ahmed E, Voit A, Klose M, Greyer M, Svatos A, Merten D, Roth M, Holmström SJM, Kothe E. (2015) Siderophore production by streptomycetes - stability and alteration of ferrihydroxamates in heavy metal contaminated soil. Env Sci Poll Res 22, 19376-19383.
Schindler F, Merbold L, Karlsson S, Sprocati AR, Kothe E (2016) Seasonal change of microbial activity in microbially aided bioremediation. J Geochem Explor, in press. doi:10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.04.001.
Beyer A, Burow K, Büchel G, Kothe E (2015) Bacterial communities in salt marine evaporate rocks and pristine Zechstein aquifers. Geomicrobiol J, DOI: 10.1080/01490451.2015.1099764.
Beyer A, Rzanny M, Weist A, Möller S, Burow K, Gutmann F, Neumann S, Lindner J, Müsse S, Brangsch H, Stoiber-Lipp J, Lonschinski M, Merten D, Büchel G, Kothe E. (2015) Aquifer community structure in dependence of lithostratigraphy in groundwater reservoirs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 19342-19351.
Phieler R, Merten D, Roth M, Büchel G, Kothe E (2015) Phytoremediation using microbially mediated metal accumulation in Sorghum bicolor. Env Sci Poll Res 22, 19408-19416.
Schütze E, Klose M, Merten D, Nietzsche S, Senftleben D, Roth M, Kothe E (2014) Growth of streptomycetes in soil and their impact on bioremediation. J Hazard Materials 267, 128-135.